International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies
2019, Vol. 7, Issue 6, Part A
Histopathology in the fish Channa punctatus, Heteropneustes fossilis and Anabas testudineus exposed to diazinon
Author(s): Mohammad Sohidul Islam, MD. Mansurul Haque, MD. Nazim Uddin and MD. Hasanuzzaman
Abstract: Pesticides deteriorate the normal function of vital organs of fishes and in case of high concentrations, it totally damaged those organs. Histological changes in gills, liver, heart, intestine and kidney of three common fish species (
Channa punctatus,
Heteropneustes fossilis and
Anabas testudineus) have been studies to observe the effect of Diazinon as it has become a very common pollutant in the aquatic environment. Six different concentrations (2.5. 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0 and 25.0 mg/l) of pesticide had been applied in the test aquaria (Chari) to experience the major alterations of the vital organs of the three treated species of fish. Lower concentrations (2.5 to 10.0 mg/l) had no remarkable effect on the treated organs, whereas, Curley gill lamellae, irregular blood vessels in the liver, muscle fiber destruction in heart, blended Submucosa and glomerular necrosis were found in
C. punctatus from 15.0 to 25.0 mg/l doses. Lamellar fusion, sinusoid vacuoles, fused villi and hemorrhagic renal tubules were observed in
H. fossilis and bent in secondary lamellae, irregular blood vessels in liver, fragmented muscle fiber in heart, ruptured villi as well as necrotic glomerular were noticed in
A. testudineus in the same doses of Diazinon. The present study demonstrated that pesticide (Diazinon) disrupted the normal function of the sensible organs of fishes by damaging them in different ways.
Related Graphics: Click here for more related graphics: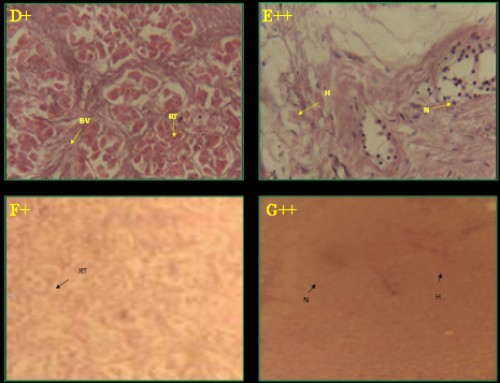 Fig. 1:
Fig. 1: Histological photomicrograph of control and diazinon affected kidney tissues of three fish species; A-C =
C. punctatus; D&E =
H. fossilis; F&G =
A. testudineus; * = control; + = 20 mg/l; ++ = 25 mg/l concentration; BC= bauman’s capsule; RT= renal tubule; BV= blood vessel; G= glomerulus; H= hemorrhage; N= necrosis
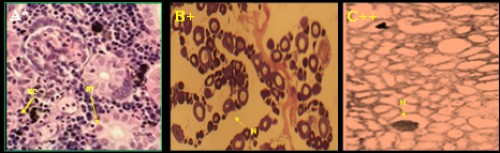 Fig. 2:
Fig. 2: Histological photomicrograph of control and diazinon affected kidney tissues of three fish species; A-C =
C. punctatus; D&E =
H. fossilis; F&G =
A. testudineus; * = control; + = 20 mg/l; ++ = 25 mg/l concentration; BC= bauman’s capsule; RT= renal tubule; BV= blood vessel; G= glomerulus; H= hemorrhage; N= necrosis
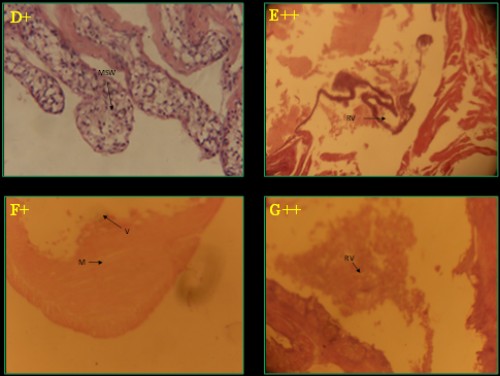 Fig. 3:
Fig. 3: Histological photomicrograph of control and diazinon affected intestine tissues of three fish species; A-C =
C. punctatus; D&E =
H. fossilis; F&G =
A. testudineus; * = control; + = 20 mg/l; ++ = 25 mg/l concentration; M= muscular tissue; S= sub mucosa; V= villi; MSW= muscularies swollen; RV= rupture of villi
Click Here
How to cite this article:
Mohammad Sohidul Islam, MD. Mansurul Haque, MD. Nazim Uddin, MD. Hasanuzzaman. Histopathology in the fish Channa punctatus, Heteropneustes fossilis and Anabas testudineus exposed to diazinon. Int J Fish Aquat Stud 2019;7(6):47-54.



