International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies
2019, Vol. 7, Issue 6, Part A
Histopathology in the fish Channa punctatus, Heteropneustes fossilis and Anabas testudineus exposed to diazinon
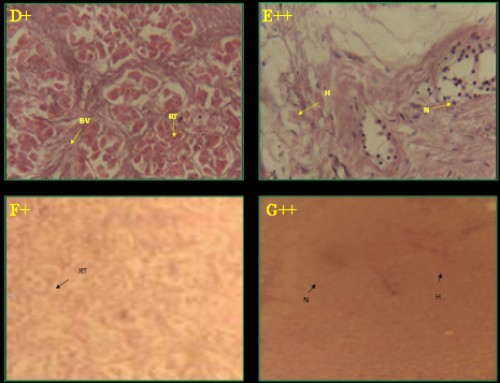 Fig. 1:
Fig. 1: Histological photomicrograph of control and diazinon affected kidney tissues of three fish species; A-C =
C. punctatus; D&E =
H. fossilis; F&G =
A. testudineus; * = control; + = 20 mg/l; ++ = 25 mg/l concentration; BC= bauman’s capsule; RT= renal tubule; BV= blood vessel; G= glomerulus; H= hemorrhage; N= necrosis
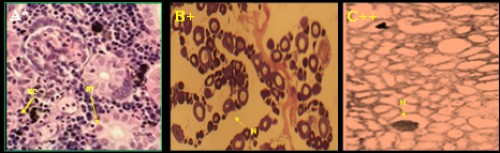 Fig. 2:
Fig. 2: Histological photomicrograph of control and diazinon affected kidney tissues of three fish species; A-C =
C. punctatus; D&E =
H. fossilis; F&G =
A. testudineus; * = control; + = 20 mg/l; ++ = 25 mg/l concentration; BC= bauman’s capsule; RT= renal tubule; BV= blood vessel; G= glomerulus; H= hemorrhage; N= necrosis
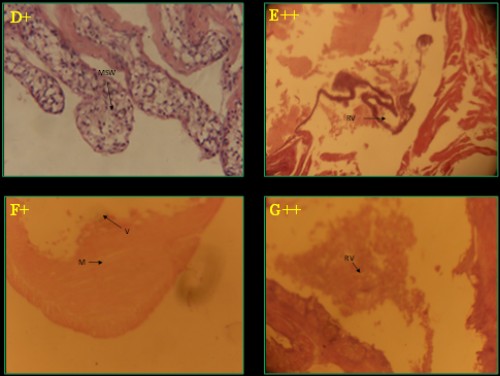 Fig. 3:
Fig. 3: Histological photomicrograph of control and diazinon affected intestine tissues of three fish species; A-C =
C. punctatus; D&E =
H. fossilis; F&G =
A. testudineus; * = control; + = 20 mg/l; ++ = 25 mg/l concentration; M= muscular tissue; S= sub mucosa; V= villi; MSW= muscularies swollen; RV= rupture of villi
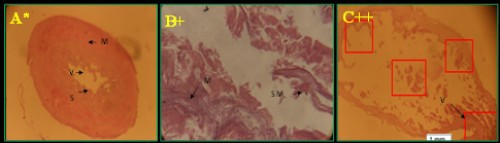 Fig. 4:
Fig. 4: Histological photomicrograph of control and diazinon affected intestine tissues of three fish species; A-C =
C. punctatus; D&E =
H. fossilis; F&G =
A. testudineus; * = control; + = 20 mg/l; ++ = 25 mg/l concentration; M= muscular tissue; S= sub mucosa; V= villi; MSW= muscularies swollen; RV= rupture of villi
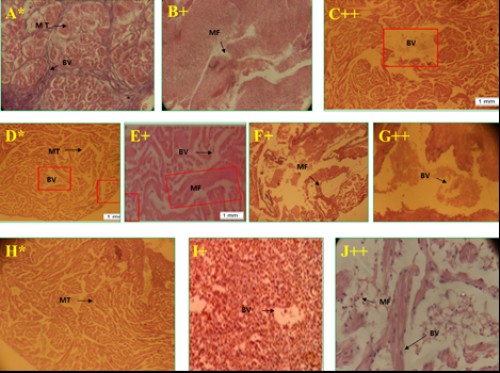 Fig. 5:
Fig. 5: Histological photomicrograph of control and diazinon affected heart tissues of three fish species; A-C =
C. punctatus; D-G =
H. fossilis; H-J =
A. testudineus; * = control; + = 20 mg/l; ++ = 25 mg/l concentration; MT= muscle tissue; BV= blood vessel; MF= muscle fiber fragmentation.
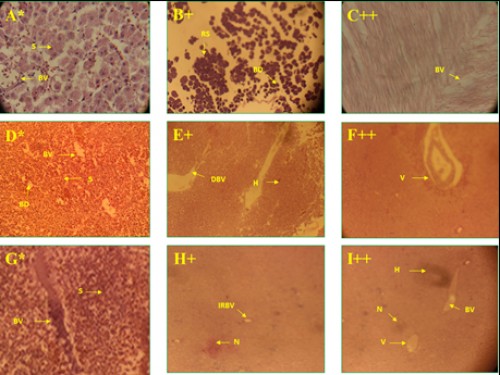 Fig. 6:
Fig. 6: Histological photomicrograph of control and diazinon affected liver tissues of three fish species; A-C =
C. punctatus; D-F =
H. fossilis; G-I =
A. testudineus; * = control; + = 20 mg/l; ++ = 25 mg/l concentration; S= sinusoids; BV= blood vessel; RS= rupture of sinusoids; BD= bile duct; DBV= destruction of bile duct; H= hemorrhage; V= vacuole; IRBV= irregular blood vessel; N= necrosis.
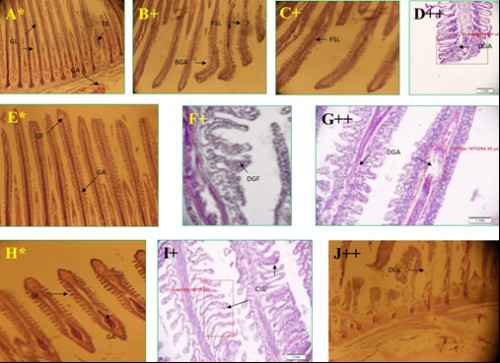 Fig. 7:
Fig. 7: Histological photomicrograph of control and diazinon affected gill tissues of three fish species; A-D =
C. punctatus; E-G =
H. fossilis; H-J =
A. testudineus; * = control, + = 20 mg/l; ++ = 25 mg/l concentration; GL= gill lamellae; GA= gill arch; TB= test buds; FSL= fusion of secondary lamellae; BGA= bend of gill arch; DGA= damage of gill arch; GF= gill filament; DGF= destruction of gill filament; CSL= curly of secondary lamellae; DGL= destruction of gill lamellae







