International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies
Volume 1, Issue 5, 2014
Copper and Cadmium induced histopathological alterations in liver of Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch) at varying water pH
Author(s): R. Paul, L. L. Guite, S. N. Ramanujam
Abstract: Histology of liver exposed to 36 hour LC50 concentration of copper sulfate (CuSO4.5H2O) and cadmium chloride (CdCl2.H2O) with varying water pH (4±0.5, 7±0.5 and 8±0.5) was studied in an air-breathing catfish (Heteropneustes fossilis). The histopathological changes observed in the liver tissue post exposure included necrosis, degradation of hepatocytes, degeneration of blood vessels, distended sinusoids with pyknotic nuclei and vacuolation of cells. The degree of damage to the liver tissue was proportional to the nominal concentrations of the metals used. Further the pH of diluent water affected the alteration more acutely signifying a synergistic effect.
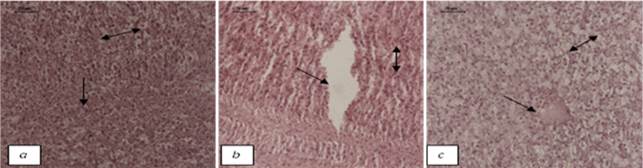
Fig: Transverse sections of H. fossilis liver at pH 7±0.5 after 36 hour-H&E-40X (a) Control: Normal hepatocytes (single headed arrow); Sinusoids (double headed arrow) (b) Copper treated: Degradation of cellular hepatocytes (single headed arrow); sinusoids with pyknotic nuclei (double headed arrow) (c) Cadmium treated: Necrosis (single headed arrow); Sinusoids (double headed arrow)
Download Full Article: Click Here
Journal is Indexed and Abstracted in following Database(s).
    |
    |
       |

